We know how frustrating it is to have a 3D printer clogged nozzle. It is something that most of us experienced.
You start your printing process.
Everything is running smoothly.
Suddenly, you start hearing a knocking or clicking sound, pointing out that something went wrong.
You approach the printer and realize that it got jammed. Your 3D filament got stuck, and your nozzle is now clogged.
If this happened to you, then you are in the right place!
Main Causes of 3D Printer Clogged Nozzles
Wrong Printing Temperature
Melting your filament at the right temperature is key to achieving great performance in your project. If the temperature is too low, it won’t melt correctly. This can cause your filament to accumulate in the inside part of the nozzle head, blocking the way out.
| 3D Filament Type | Printing Temperature |
| PVA | 160-190°C |
| PLA | 180-220°C |
| ABS | 200-250°C |
| PETG | 220-255°C |
| TPE | 210-240°C |
| TPU | 230-250°C |
| ASA | 230-260°C |
If this is not solved quickly, then you will most likely have your 3D printer nozzle clogged with material. Once it gets blocked, you will have to remove it. You will also notice that whenever you try to start your print process it won’t extrude at the beginning.
On the other side, melting at higher temperatures than you should, especially with PLA, can cause a “heat creep”. This means that your melting area is extended far back and upward toward your hot end.
This will eventually soften your filament before getting to your extrusion zone, increasing the chances of that filament getting stuck upward in your melting zone.
Check Nozzle Height
Nozzles need to be at the correct height from the surface to print your project successfully. In addition, things can go wrong if you have it too high or too low.
On the one hand, if your nozzle is too high, your filament will have to travel a longer distance before it reaches the printing surface. Therefore, the filament will most likely suffer from cooler temperatures, making it more difficult to adhere.
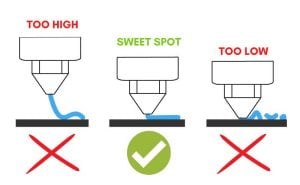
On the other hand, if your printer nozzle is too low, there will be no room for your filament to get extruded, so it will over-extrusion and begin to pile up inside and clog the nozzle.
To fix this problem, make sure that your print bed is leveled correctly and that your starting Z coordinates are sufficient to allow room for extrusion.
Contaminants
External factors such as dirt, dust, humidity, and other contaminants can adhere to your filament when traveling down the hot end. These contaminants burn in the heated nozzle and start to stick inside the surface of the nozzle, turning into carbon.
You will start to notice this problem when the flow of your filament starts getting narrower. This is because enough carbon was created inside the nozzle, difficulting your filament to flow. In the end, you will most likely suffer from a 3D printer clogged nozzle.
To avoid this, consider implementing or upgrading your filament storage solutions.
Solutions for 3D Printer Clogged Nozzles
Here are two things that you can do to fix your 3D printer nozzle clogging.
Needles & Guitar Strings to Unclog Nozzles
To use this method, you will have to be careful. First, choose an acupuncture needle or a High E steel guitar string. Then, heat the hot end that you will introduce in your clogged nozzle with the printing temperature of the material that’s inside (PLA – 190°C–230°C).

After than, using a pair of pliers, carefully introduce your selected instrument to unclog your nozzle.
The Solvent Method
If you are printing a material that can be soluble, then removing the nozzle and soaking it in a solvent solution might be your answer.

Different materials have different solvent solutions. For example, dip printer nozzles in a bowl of acetone to remove PLA remainings in the clogged nozzle.
High-Quality Nozzles
Even if you unload your filament when you are done printing and you are careful with your 3D printer, you might encounter this situation if you don’t have high-quality printer nozzles.
This is why we recommend using Nano-Diamondized printer nozzles.

These printing nozzles show no change throughout the lifecycle of the nozzle. With minimal temperature drifts, this type of nozzle exhibits better thermodynamics.
